Determinan Stunting Balita di Wilayah Kerja Puskesmas Moutong, Kabupaten Parigi Moutong, Sulawesi Tengah
Determinants of Toddler Stunting in the Working Area of the Moutong Health Center, Parigi Moutong Regency, Central Sulawesi
Keywords:
Determinant, Stunting, Toddler, moutongAbstract
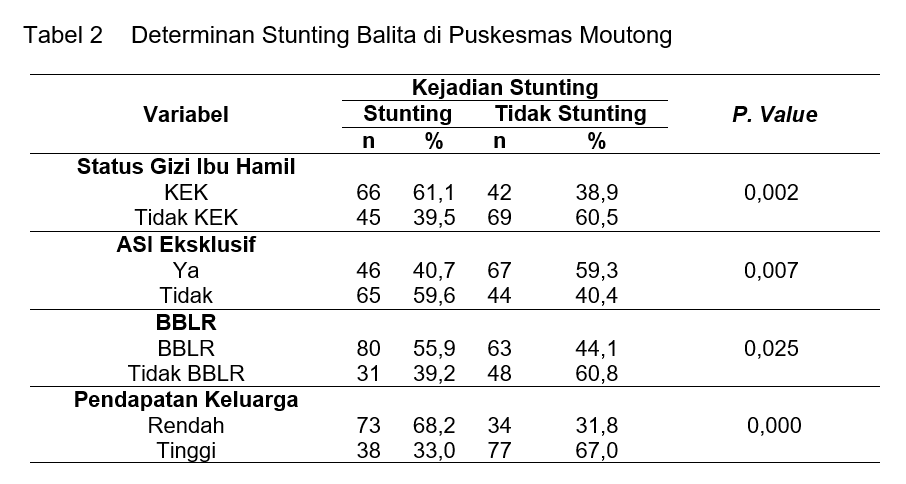
Introduction: The causes of stunting are maternal nutritional status, non-exclusive breastfeeding, low birth weight, and family income. This study aims to analyze the determinants of stunting among toddlers at Moutong Health Center in 2020. The research method used was cross-sectional. The study was conducted from March 3 to March 21, 2020, at Moutong Health Center, Parigi Moutong, Central Sulawesi. The data used in this study were secondary data from 2020. The sample size consisted of 222 toddler respondents. Simple random sampling technique was employed. Data analysis was performed using chi-square test and odds ratio. The results of the study showed that the highest prevalence of stunting was found among pregnant women with low nutritional status (61.1%), non-exclusive breastfeeding (59.6%), low birth weight (55.9%), and low family income (68.2%). Chi-square test indicated that all variables had significant values (<0.05). Multivariate analysis showed an odds ratio of 4.5 for low birth weight and stunting. In conclusion, this study found that low birth weight had a 4.5 times higher risk of stunting. It is recommended that healthcare professionals conduct education, prevention, and early detection of stunting, monitor the provision of maternal and child nutrition programs to pregnant women and toddlers, and provide assistance to low-income families or those who are unable to afford proper nutrition.
Downloads
References
Abbas, F., Kumar, R., Mahmood, T., & Somrongthong, R. (2021). Impact of children born with low birth weight on stunting and wasting in Sindh province of Pakistan : a propensity score matching approach. Scientific Reports, 11(19932), 1–10. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-021-98924-7
Agustina, W., & Fathur, F. (2022). Ibu Hamil KEK, Berat Bayi Lahir Rendah dan Tidak ASI Eksklusif sebagai Faktor Risiko Terjadinya Stunting. Jurnal Kesehatan Tambusai, 3(1), 263–270. https://doi.org/10.31004/jkt.v3i1.4015
Alba, A. D., Suntara, D. A., & Siska, D. (2021). Berat Badan Lahir Rendah. Jurnal Inovasi Penelitian, 1(12), 6. https://doi.org/10.47492/jip.v1i12.540
Alfarisi, R., Nurmalasari, Y., & Nabilla, S. (2019). Status Gizi Ibu Hamil Dapat Menyebabkan Kejadian Stunting Pada Balita. JKM (Jurnal Kebidanan Malahayati), 5(3), 271–278. Retrieved from https://core.ac.uk/download/pdf/230556152.pdf
Anggryni, M., Mardiah, W., Hermayanti, Y., Rakhmawati, W., Ramdhanie, G. G., & Mediani, H. S. (2021). Faktor Pemberian Nutrisi Masa Golden Age dengan Kejadian Stunting pada Balita di Negara Berkembang. Jurnal Obsesi : Jurnal Pendidikan Anak Usia Dini, 5(2), 1764–1776. https://doi.org/10.31004/obsesi.v5i2.967
Dinas Kesehatan Parigi Moutong. (2020). Analisis Indikator Stunting 1 Tahun 2020. Parigi: Dinas Kesehatan parigi Moutong.
Ekayanthi, N. W. D., & Suryani, P. (2019). Edukasi Gizi pada Ibu Hamil Mencegah Stunting pada Kelas Ibu Hamil. Jurnal Kesehatan, 10(3), 312. Retrieved from https://ejurnal.poltekkes-tjk.ac.id/index.php/JK/article/view/1389
Fitri, L. (2018). Stunting Di Puskesmas Lima Puluh Pekanbaru. Jurnal Endurance, 3(1), 131–137. Retrieved from http://ejournal.lldikti10.id/index.php/endurance/article/viewFile/1767/930
García Cruz, L. M., González Azpeitia, G., Reyes Súarez, D., Santana Rodríguez, A., Loro Ferrer, J. F., & Serra-Majem, L. (2017). Factors associated with stunting among children aged 0 to 59 months from the central region of Mozambique. Nutrients, 9(5), 1–16. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu9050491
Hadi, M. I., Kumalasari, M. L. F., & Kusumawati, E. (2019). Faktor Risiko yang Berhubungan dengan Kejadian Stunting di Indonesia: Studi Literatur. Journal of Health Science and Prevention, 3(2), 86–93. https://doi.org/10.29080/jhsp.v3i2.238
Halli, S. S., Biradar, R. A., & Prasad, J. B. (2022). Low Birth Weight, the Differentiating Risk Factor for Stunting among Preschool Children in India. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 19(7), 3751. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph19073751
Ikram. (2022). Prevalensi Stunting Sulteng 31,26 Persen dan di Atas Rata-Rata Nasional. Retrieved January 3, 2023, from Media Indonesia website: https://mediaindonesia.com/nusantara/513183/sulteng-fokus-penanganan-masalah-stunting#:~:text=Rusdy menjelaskan%2C hasil survei status,nasional sebesar 24%2C4 persen.
Kamal Windasari Dewi Purnama ; et all, I. S. L. S. (2020). Faktor Hubungan dengan Kejadian Stunting di Puskesmas Tamalate Kota Makassar (Factors related to the incidence of stunting at the Tamalate health center in Makassar city ). Aceh Nutrition Jurnal, 1(5), 27–34. Retrieved from http://dx.doi.org/10.30867/action.v5i1.193
Kemenkes RI. Peraturan Menteri Kesehatan Republik Indonesia Nomor 51 Ttahun 2016 tentang Standar Produk Suplementasi Gizi. , Kemenkes RI § (2016).
Kemenkes RI. (2018). Hasil Riset Kesehatan Dasar Tahun 2018. Kementrian Kesehatan RI, 53(9), 1689–1699. Retrieved from https://kesmas.kemkes.go.id/assets/upload/dir_519d41d8cd98f00/files/Hasil-riskesdas-2018_1274.pdf
Lestari, P. D., Rohmah, N., & Utami, R. (2019). Hubungan Status Gizi Ibu Saat Hamil Dengan Kejadian Stunting Pada Balita. Fakultas Ilmu Kesehatan Universitas Muhammadiyah Jember, 26, 1–9. Retrieved from http://repository.unmuhjember.ac.id/5047/11/k.
Liza Munira, S. (2023). Disampaikan pada Sosialisasi Kebijakan Intervensi Stunting Jakarta, 3 Februari 2023 Hasil Survei Status Gizi Indonesia (SSGI) 2022. Retrieved from https://promkes.kemkes.go.id/materi-hasil-survei-status-gizi-indonesia-ssgi-2022
Mediani, H. S. (2020). Predictors of Stunting Among Children Under Five Year of Age in Indonesia: A Scoping Review. Global Journal of Health Science, 12(8), 83. https://doi.org/10.5539/gjhs.v12n8p83
Mugianti, S., Mulyadi, A., Anam, A. K., & Najah, Z. L. (2018). Faktor Penyebab Anak Stunting Usia 25-60 Bulan di Kecamatan Sukorejo Kota Blitar. Jurnal Ners Dan Kebidanan (Journal of Ners and Midwifery), 5(3), 268–278. https://doi.org/10.26699/jnk.v5i3.art.p268-278
Nurmalasari, Y., Anggunan, A., & Febriany, T. W. (2020). Hubungan Hubungan Tingkat Pendidikan Ibu Dan Pendapatan Keluarga Dengan Kejadian Stunting Pada Anak Usia 6-59 Bulantingkat Pendidikan Ibu Dan Pendapatan Keluarga Dengan Kejadian Stunting Pada Anak Usia 6-59 Bulan Di Desa Mataram Ilir Kecamatan Seputih Sur. Jurnal Kebidanan Malahayati, 6(2), 205–211. https://doi.org/10.33024/jkm.v6i2.2409
Rahmad, A. H. A. L., & Miko, A. (2016). Kajian Stunting pada Anak Balita Berdasarkan Pola Asuh dan Pendapatan Keluarga di Kota Banda Aceh. Jurnal Kesmas Indonesia, 8(2), 63–79. Retrieved from http://jos.unsoed.ac.id/index.php/kesmasindo/article/view/151/60
Saadong, D., B, S., Nurjaya, N., & Subriah, S. (2021). BBLR, Pemberian ASI Eksklusif, Pendapatan Keluarga, dan Penyakit Infeksi Berhubungan dengan Kejadian Stunting. Jurnal Kesehatan Manarang, 7(Khusus), 52. https://doi.org/10.33490/jkm.v7ikhusus.374
Saparwati, I. P. S. F. W. M. (2020). Riwayat Pemberian ASI Eksklusif dengan Kejadian Stunting pada Balita Usia 24-60 Bulan. JIDAN (Jurnal Ilmiah Bidan), 7(1), 8–13. https://doi.org/10.47718/jib.v7i1.878
Taqwin, T., Linda, L., & Ifda, N. (2022). Peningkatan Minat Ibu Hamil Memberikan ASI Eksklusif melalui Promosi ASI Eksklusif. Jurnal Bidan Cerdas, 4(2), 111–119. https://doi.org/10.33860/jbc.v4i2.1130
Taqwin, T., Linda, L., Kusika, S. Y., Ramadhan, K., Radhiah, S., & Bohari, B. (2022). The Effectiveness of Baby Massage in Stunting Prevention: Study Based on Body Length Gain in Infants aged 0–3 Months. Open Access Macedonian Journal of Medical Sciences, 10(E), 1184–1189. https://doi.org/10.3889/oamjms.2022.8906
Taqwin, T., Ramadhan, K., Hadriani, H., Nasrul, N., Hafid, F., & Efendi, F. (2020). Prevalence of Stunting among 10-Year Old Children in Indonesia. Journal of Global Pharma Technology, 12(02), 768–773. Retrieved from http://www.jgpt.co.in/index.php/jgpt/article/view/3375/2658
Tesfaye, A., & Egata, G. (2022). Stunting and associated factors among children aged 6–59 months from productive safety net program beneficiary and non-beneficiary households in Meta District, East Hararghe zone, Eastern Ethiopia: a comparative cross-sectional study. Journal of Health, Population and Nutrition, 41(1), 13. https://doi.org/10.1186/s41043-022-00291-0
Yazew, T. (2022). Risk Factors of Stunting and Wasting among Children Aged 6–59 Months in Household Food Insecurity of Jima Geneti District, Western Oromia, Ethiopia: An Observational Study. Journal of Nutrition and Metabolism, 2022, 1–8. https://doi.org/10.1155/2022/3981417
Zogara, A. U., & Pantaleon, M. G. (2020). Faktor-faktor yang Berhubungan dengan Kejadian Stunting pada Balita. Jurnal Ilmu Kesehatan Masyarakat, 9(02), 85–92. https://doi.org/10.33221/jikm.v9i02.505
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
Copyright (c) 2023 Taqwin, Anna Veronica Pont, Yuyun Iskandar

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 4.0 International License.
Authors who publish with Jurnal Bidan Cerdas agree to the following terms:
- Authors retain copyright and grant the journal right of first publication with the work simultaneously licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY-SA 4.0) that allows others to share the work with an acknowledgment of the work's authorship and initial publication in this journal.
- Authors are able to enter into separate, additional contractual arrangements for the non-exclusive distribution of the journal's published version of the work (e.g., post it to an institutional repository or publish it in a book), with an acknowledgment of its initial publication in this journal.
- Authors are permitted and encouraged to post their work online (e.g., in institutional repositories or on their website) prior to and during the submission process, as it can lead to productive exchanges, as well as earlier and greater citation of published work.

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-Share Alike 4.0 International License
You are free to:
- Share, copy and redistribute the material in any medium or format
- Adapt, remix, transform, and build upon the material for any purpose, even commercially.
- The licensor cannot revoke these freedoms as long as you follow the license terms.




