Gambaran Kejadian Risiko 4T pada Ibu Hamil di Puskesmas Jatinangor
Keywords:
pregnancy, too young, too old, too close, too many, high risk pregnancyAbstract
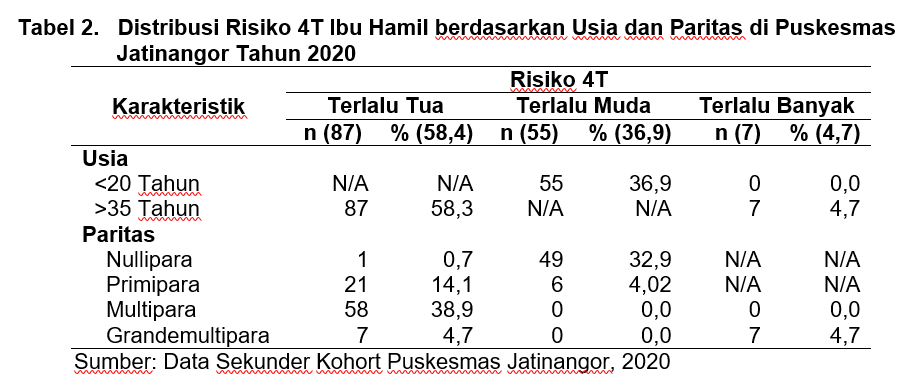
Introduction: High-risk pregnancies are found in pregnant women who are too old, too young, too many, and too close (4T). Many risk factors become screening/early detection of pregnant women in the Poedji Rochjati scorecard, including maternal age <16 years, maternal age >35 years, and mothers who have children 4 or more. Objective: The aim of this study was to describe the 4T risk incidence in pregnant women at the Jatinangor Community Health Center in 2020. Methods: The type of research used was descriptive-analytic with a quantitative approach and cross-sectional design. The population in this study were all pregnant women who were in Jatinangor Health Center. January-September 2020 period, amounting to 2357 people, using accidental sampling technique and obtained a total sample of 149 people. Data analysis using descriptive data analysis with frequency distribution. Results: The results showed that respondents who had the highest risk of 4T were 63.19% at the age of more than 35 years, and multiparity of 43.62%. Conclusion: In this study, it was found that the incidence of 4T risk in pregnant women at the Jatinangor Health Center in 2020 was mostly at the risk of being too old by 58.3% which was dominated by multiparity.
Downloads
References
Arisandi, M. E., Anita, A., & Abidin, Z. (2016). Faktor-Faktor yang Berhubungan dengan Kejadian Komplikasi Persalinan di Wilayah Kerja Puskesmas Tanjung Bintang Kabupaten Lampung Selatan. Jurnal Kesehatan, 7(2), 204. https://doi.org/10.26630/jk.v7i2.189
Bappeda Kabupaten Sumedang, B. K. S. (2018). Gambaran Umum Kondisi Daerah. Rencana Pembangunan Jangka Menengah Daerah (RPJMD) Kabupaten Sumedang. http://bappppeda.sumedangkab.go.id/file/BAB II GAMBARAN UMUM KONDISI DAERAH.pdf
BKKBN. (2018). Sosialisasi 4T. Http://Kampungkb.Bkkbn.Go.Id/PostSlider/4536/26070. http://kampungkb.bkkbn.go.id/
Dien, G. A. N. (2015). Kehamilan Risiko Tinggi Di Puskesmas Lubuk Gadang Kabupaten Solok Selatan. Jurnal Kesehatan Masyarakat Andalas, 9(1), 23–28.
Kemenkes RI. (2018). Profil Kesehatan Indonesia 2018 [Indonesia Health Profile 2018]. http://www.depkes.go.id/resources/download/pusdatin/profil-kesehatan-indonesia/Data-dan-Informasi_Profil-Kesehatan-Indonesia-2018.pdf
Kemenkes RI. (2019). Profil Kesehatan Indonesia Tahun 2019. In Kementrian Kesehatan Repoblik Indonesia (Vol. 42, Issue 4).
Komariah, S., & Nugroho, H. (2020). Hubungan Pengetahuan, Usia Dan Paritas Dengan Kejadian Komplikasi Kehamilan Pada Ibu Hamil Trimester Iii Di Rumah Sakit Ibu Dan Anak Aisyiyah Samarinda. KESMAS UWIGAMA: Jurnal Kesehatan Masyarakat, 5(2), 83. https://doi.org/10.24903/kujkm.v5i2.835
Kurniasari, D., JURNAL, F. A.-H., & 2015, undefined. (2015). Hubungan Usia, Paritas Dan Diabetes Mellitus Pada Kehamilan Dengan Kejadian Preeklamsia Pada Ibu Hamil Di Wilayah Kerja Puskesmas Rumbia Kabupaten. Ejurnalmalahayati.Ac.Id, 9(3), 142–150. http://ejurnalmalahayati.ac.id/index.php/holistik/article/view/232
Manuaba. (2007). Pengantar kuliah Obstetri. Buku Kedokteran EGC.
Maria RA. (2011). Gambaran faktor ibu hamil resiko tinggi tahun 2005-2010 (Di Polindes Sambikerep Kecamatan Rejoso Kabupaten Nganjuk). Jurnal Penelitian Kesehatan Suara Forikes, 2(1). http://fmipa.umri.ac.id/wp-content/uploads/2016/06/novelia-kumpulan-jurnal.pdf#page=5
Maryunani A. (2016). Buku Praktis Kehamilan dan Persalinan Patologis (Resiko Tinggi dan Komplikasi). TIM.
Mukhammad ABF. (2016). Hubungan Antara Pengetahuan dan Sikap dengan Perilaku Konsumsi Jajanan Sehat Di MI Sulaimaniyah Mojoagung Jombang. Airlangga University.
Nuraisyah, S. (2019). Gambaran Pengetahuan Ibu Hamil Tentang Risiko 4T Desa Jahiang Kecamatan Salawu Kabupaten Tasikmalaya. Jurnal Kesehatan Bakti Tunas Husada: Jurnal Ilmu-Ilmu Keperawatan, Analis Kesehatan Dan Farmasi, 19(2), 304. https://doi.org/10.36465/jkbth.v19i2.506
P.Senewe, F., & Sulistiyowati, N. (2004). Faktor-Faktor Yang Berhubungan dengan komplikasi persalinan tiga tahun terakhir di Indonesia. In Puslitbang Ekologi Kesehatan (Vol. 32, Issue 2, pp. 83–91).
Rochjati, P. (2004). Skrining Antenatal Pada Ibu Hamil (F. K. U. Airlangga (ed.); 2nd ed.). Fakultas Kedokteran Universitas Airlangga, Airlangga University press.
Wellings, K. E. all. (2013). The prevalence of unplanned pregnancy and associated factors in Britain: findings from the third National Survey of Sexual Attitudes and Lifestyles (Natsal-3). Journal Research Department of Infection and Population Health, University College London. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3898922/
Widarta GD, Laksana MAC, Sulistyono A, P. W. (2015). Deteksi Dini Risiko Ibu Hamil dengan Kartu Skor Poedji Rochjati dan Pencegahan Faktor Empat Terlambat. Majalah Obstetri & Ginekologi, 1(23), 28–32. https://doi.org/http://dx.doi.org/10.20473/mog.V23I12015.28-32
Winkjosastro, H. (2010). Ilmu Kebidanan. Yayasan Bina Pustaka Sarwono Prawirohardjo.
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
Copyright (c) 2021 Authors

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 4.0 International License.
Authors who publish with Jurnal Bidan Cerdas agree to the following terms:
- Authors retain copyright and grant the journal right of first publication with the work simultaneously licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY-SA 4.0) that allows others to share the work with an acknowledgment of the work's authorship and initial publication in this journal.
- Authors are able to enter into separate, additional contractual arrangements for the non-exclusive distribution of the journal's published version of the work (e.g., post it to an institutional repository or publish it in a book), with an acknowledgment of its initial publication in this journal.
- Authors are permitted and encouraged to post their work online (e.g., in institutional repositories or on their website) prior to and during the submission process, as it can lead to productive exchanges, as well as earlier and greater citation of published work.

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-Share Alike 4.0 International License
You are free to:
- Share, copy and redistribute the material in any medium or format
- Adapt, remix, transform, and build upon the material for any purpose, even commercially.
- The licensor cannot revoke these freedoms as long as you follow the license terms.




