Determinan yang Berhubungan dengan Upaya Pencegahan Infeksi Menular Seksual pada Wanita Pekerja Seks di Jakarta Timur
Determinants Related to Efforts for Prevent Sexually Transmitted Infections among Female Sex Workers in East Jakarta
Keywords:
Female sex workers, sexually transmitted infections, STIAbstract
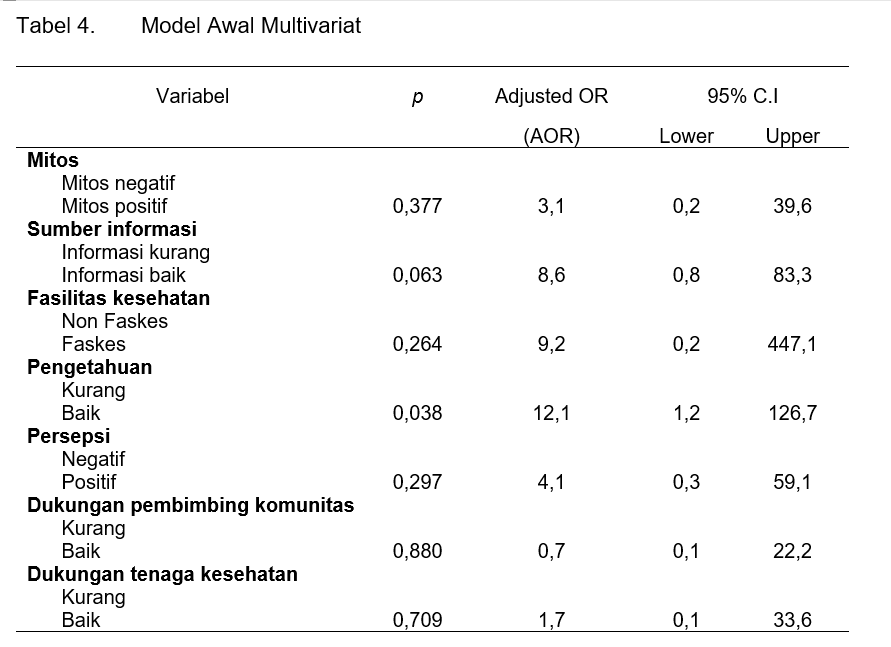
Introduction: Female sex workers (FSWs) are high-risk group for exposure to STIs and HIV. FSWs are particularly vulnerable to STIs, HIV. Only about one in three FSWs receive adequate STIs, HIV prevention services and medical care. Objective: to analyze the relationship between knowledge, perceptions and support of community counselors on STIs prevention in FSWs. Method: Quantitative research with analytic cross-sectional design. The population of this study is female sex workers in the Jingga Cipinang Community, East Jakarta. The sampling technique used was snowball sampling. Data were analyzed by chi square test and logistic regression risk model. Results: Perception variables, support from community counselors and support from health workers are associated with STIs prevention in FSWs. The results of the analysis showed that the most dominant variable was knowledge (p=0,0001) after being controlled by the information source variable, with the OR value of the knowledge variable 56.2. The multivariate model can explain that FSWs who have good knowledge will do 56 times better to prevent STIs than those whose knowledge is less after being controlled by the variable information sources. Conclusions: Knowledge of sexual and reproductive health (SRH) should reflect two main topics, namely how to promote efforts to prevent and protect women from STIs.
ABSTRAK
Pendahuluan: Wanita pekerja seks (WPS) merupakan salah satu kelompok risiko tinggi terpapar IMS dan HIV. WPS sangat rentan terhadap HIV, hanya sekitar satu dari tiga WPS menerima layanan pencegahan HIV yang memadai dan perawatan medis. Tujuan: untuk menganalisis hubungan pengetahuan, persepsi dan dukungan pembimbing komunitas terhadap pencegahan IMS padaWPS. Metode: Penelitian kuantitatif dengan desain cross-sectional yang bersifat analitik. Populasi penelitian ini adalah Wanita pekerja seks di Komunitas Jingga Cipinang Jakarta Timur. Teknik pengambilan sampling menggunakan snowball sampling. Data dianalisis dengan uji chi square dan regresi logistic model risiko. Hasil: Variabel persepsi, dukungan pembimbing komunitas dan dukungan tenaga kesehatan berhubungan dengan pencegahan IMS pada wanita pekerja seks (WPS). Hasil analisis didapatkan variabel yang paling dominan adalah pengetahuan (p=0,0001) setelah dikontrol variabel sumber informasi, dengan nilai OR dari variabel pengetahuan 56,2. Model multivariate tersebut dapat dijelaskan bahwa WPS yang mempunyai pengetahuan baik akan melakukan pencegahan infeksi menular seksual 56 kali lebih baik dibandingkan yang pengetahuannya kurang setelah dikontrol oleh variabel sumber informasi. Kesimpulan: Pengetahuan kesehatan reproduksi dan seksual sebaiknya mencerminkan dua topik utama, yaitu bagaimana caranya mempromosikan upaya pencegahan dan melindungi wanita dari IMS.
Downloads
References
Argento, E., Goldenberg, S., & Shannon, K. (2019). Preventing sexually transmitted and blood borne infections (STBBIs) among sex workers: A critical review of the evidence on determinants and interventions in high-income countries. Journal BMC Infectious Diseases, 19(1). https://doi.org/10.1186/s12879-019-3694-z
Aryani, D., Mardiana, M., & Ningrum, D. N. A. (2015). Perilaku Pencegahan Infeksi Menular Seksual Pada Wanita Pekerja Seksual Kabupaten Tegal. Jurnal Kesehatan Masyarakat, 10(2), 160. https://doi.org/10.15294/kemas.v10i2.3377
Bailey, A. (2019). Analysing Semi-Structured Interviews to Explore Sexual Decision-Making and HIV/STI Risk Perception Among Female Sex Workers: A Grounded Theory Approach. SAGE Publications, Ltd. https://doi.org/10.4135/9781526483812
Becquet, V., Nouaman, M., Plazy, M., Masumbuko, J. M., Anoma, C., Kouame, S., Danel, C., Eholie, S. P., & Larmarange, J. (2020). Sexual health needs of female sex workers in Côte d’Ivoire: a mixed-methods study to prepare the future implementation of pre-exposure prophylaxis (PrEP) for HIV prevention. BMJ Open, 10(1), e028508. https://doi.org/10.1136/bmjopen-2018-028508
Chow, E. P. F., Tung, K., Tucker, J. D., Muessig, K. E., Su, S., Zhang, X., Jing, J., & Zhang, L. (2015). Behavioural interventions improve condom use and hiv testing uptake among female sex workers in china: a systematic review and meta-analysis. In Sexually Transmitted Infections (Vol. 91). BMJ. https://doi.org/10.1136/sextrans-2015-052270.146
Dewi, D. M. S. K., Wulandari, L. P. L., & Wirawan, D. N. (2019). Determinan Sosial Kerentanan Perempuan Terhadap Penularan Ims Dan Hiv. Journal of Public Health Research and Community Health Development, 2(1), 22. https://doi.org/10.20473/jphrecode.v2i1.16250
Dinkes DKI. (2017). Profil Kesehatan DKI Jakarta Tahun 2017.
Januraga, P. P., Gesesew, H. A., & Ward, P. R. (2020). Trust as a Determinant Factor for Condom Use among Female Sex Workers in Bali, Indonesia. In Tropical Medicine and Infectious Disease (Vol. 5, Issue 3, p. 131). MDPI AG. https://doi.org/10.3390/tropicalmed5030131
Januraga, P. P., Mooney‐somers, J., Gesesew, H. A., & Ward, P. R. (2020). The logic of condom use in female sex workers in Bali, Indonesia. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 17(5). https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph17051627
Juliastika, J., Korompis, G. E. ., & Ratag, B. . (2012). Hubungan Pengetahuan tentang HIV/AIDS dengan Sikap dan Tindakan Penggunaan Kondom Pria pada Wanita Pekerja Seks di Kota Manado Juliastika*, Grace E. C. Korompis*, Budi T. Ratag* * Fakultas Kesehatan Masyarakat Universitas Sam Ratulangi Manado. Kesmas2, 1(1), 15–20.
Keamogetse, S., & Gorata, D. M. (2017). Factors associated with HIV testing among female sex workers in Botswana. In Journal of AIDS and HIV Research. 9(2), 42–51. https://doi.org/10.5897/jahr2016.0404
Kementrian Kesehatan Republik Indonesia. (2018). Profil Kesehatan Indonesia 2018. Jakarta: Kementerian Kesehatan R.I. https://pusdatin.kemkes.go.id/resources/download/pusdatin/profil-kesehatan-indonesia/PROFIL_KESEHATAN_2018_1.pdf
Khanam, R., Reza, M., Ahmed, D., Rahman, M., Alam, M. S., Sultana, S., Alam, A., Khan, S. I., Mayer, K. H., & Azim, T. (2017). Sexually Transmitted Infections and Associated Risk Factors Among Street-Based and Residence-Based Female Sex Workers in Dhaka, Bangladesh. In Sexually Transmitted Diseases (Vol. 44, Issue 1, pp. 22–29). Ovid Technologies (Wolters Kluwer Health). https://doi.org/10.1097/olq.0000000000000536
Matahari, R. (2015). Studi Kualitatif Mengenai Persepsi Dan Perilaku Seksual Wanita Pekerja Seks Komersial (Psk) Dalam Upaya Pencegahan Ims Di Kota Semarang Tahun 2012. Jurnal Kesehatan Reproduksi, 3(3 Des), 113–123. https://doi.org/10.22435/jkr.v3i3Des.3914.113-123
Mujayanto, R., & Wardhana, E. S. (2019). Sexual Behavior and Knowledge Level of Commercial Sex Workers Influence The Spread of Sexually Transmitted Infections. In ODONTO : Dental Journal (Vol. 6, Issue 2, p. 107). Universitas Islam Sultan Agung. https://doi.org/10.30659/odj.6.2.107-112
Murtono, D. (2019). Faktor Determinan Konsistensi Pemakaian Kondom Pada Pekerja Seks Perempuan. Jurnal Litbang: Media Informasi Penelitian, Pengembangan Dan IPTEK, 15(1), 27–38. https://doi.org/10.33658/jl.v15i1.129
Omidi, T., Mohammadian-khoshnoud, M., & Mohammadi, Y. (2020). Identifying Barriers to Condom Use Among Female Sex Workers: a Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. Research Square. https://doi.org/10.21203/rs.3.rs-48093/v1
Parcesepe, A. M., L’Engle, K. L., Martin, S. L., Green, S., Suchindran, C., & Mwarogo, P. (2016). Early sex work initiation and condom use among alcohol-using female sex workers in Mombasa, Kenya: a cross-sectional analysis. In Sexually Transmitted Infections (Vol. 92, Issue 8, pp. 593–598). BMJ. https://doi.org/10.1136/sextrans-2016-052549
Purnamawati, D. (2013). Perilaku Pencegahan Penyakit Menular Seksual di Kalangan Wanita Pekerja Seksual Langsung Behavioral Prevention of Sexual Transmitted Disease among Direct Female. Kesmas, Jurnal Kesehatan Masyarakat Nasional, 7(11), 514–521. http://dx.doi.org/10.21109/kesmas.v7i11.365
Syarifah, S., Demartoto, A., & Dharmawan, R. (2018). Determinants of Safe Sex Behavior for Preventing Sexually Transmitted Infection in Female Sex Workers In Surakarta. In Revitalizing Family Planning Program and Women’s Empowerment for the Improvement of Population Well-being and Economic Development. Masters Program in Public Health, Universitas Sebelas Maret. https://doi.org/10.26911/mid.icph.2018.02.14
Tayerih, K., Bayat Jozani, Z., Golchehregan, H., Rostam-Afshar, Z., Taj, L., Ahsani Nasab, S., Foroughi, M., Mirzapour, P., Mohraz, M., Mahmoodi, Z., Talebi, Z., & Haji Abdolbaghi, M. (2019). Woman’s Sexual Health Knowledge and Needs Assessment in Behavioral Clinics and Shelters in Tehran. Journal of Family & Reproductive Health, 13(1). https://doi.org/10.18502/jfrh.v13i1.1610
Tokar, A., Sazonova, I., Mishra, S., Smyrnov, P., Saliuk, T., Lazarus, J. V, Broerse, J. E. W., Roura, M., Blanchard, J., & Becker, M. L. (2019). HIV testing behaviour and HIV prevalence among female sex workers in Ukraine: findings from an Integrated Bio-Behavioural Survey, 2013–2014. In Sexually Transmitted Infections (Vol. 95, Issue 3, pp. 193–200). BMJ. https://doi.org/10.1136/sextrans-2018-053684
Workie, H. M., Kassie, T. W., & Hailegiyorgis, T. T. (2019). Knowledge, risk perception, and condom utilization pattern among female sex workers in Dire Dawa, Eastern Ethiopia 2016: A cross-sectional study. Pan African Medical Journal, 32, 1–14. https://doi.org/10.11604/pamj.2019.32.185.16574
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
Copyright (c) 2022 Authors

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 4.0 International License.
Authors who publish with Jurnal Bidan Cerdas agree to the following terms:
- Authors retain copyright and grant the journal right of first publication with the work simultaneously licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY-SA 4.0) that allows others to share the work with an acknowledgment of the work's authorship and initial publication in this journal.
- Authors are able to enter into separate, additional contractual arrangements for the non-exclusive distribution of the journal's published version of the work (e.g., post it to an institutional repository or publish it in a book), with an acknowledgment of its initial publication in this journal.
- Authors are permitted and encouraged to post their work online (e.g., in institutional repositories or on their website) prior to and during the submission process, as it can lead to productive exchanges, as well as earlier and greater citation of published work.

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-Share Alike 4.0 International License
You are free to:
- Share, copy and redistribute the material in any medium or format
- Adapt, remix, transform, and build upon the material for any purpose, even commercially.
- The licensor cannot revoke these freedoms as long as you follow the license terms.




