Posisi Ibu Hamil Memengaruhi Akurasi Pengukuran Kesejahteraan Janin
Position of Pregnant Women Effects on Accuracy of Fetal Heart Rate Measurement
Keywords:
Mother’s position, fetal heart rate, pregnantAbstract
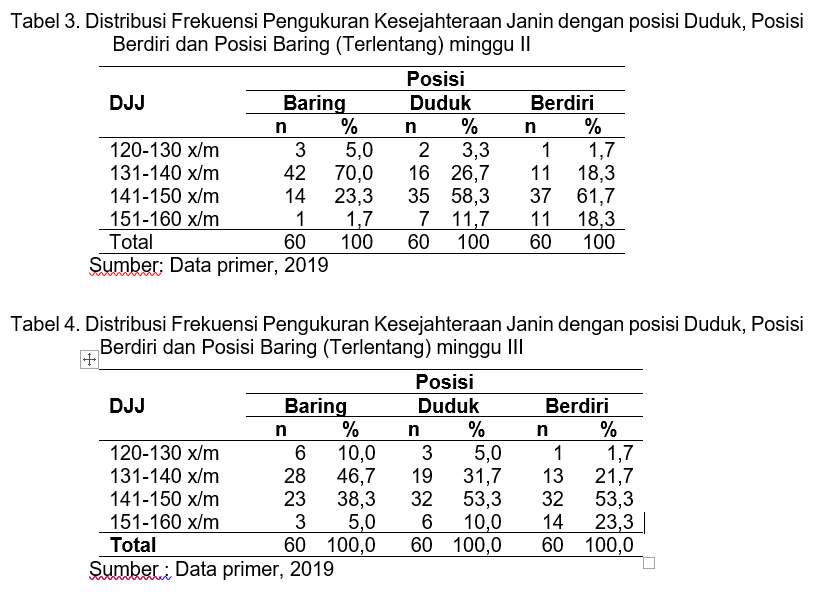
During pregnancy, the fetal heart rate is a picture of the well-being of the fetus in the womb. The mother's position affects the results of the assessment when taking measurements of the fetal heart rate. The purpose of this study is to determine the accuracy of the measurement of fetal well-being based on the position of pregnant women. This type of research is analytic observational in Wajo Health Center, Katobengke Health Center, and Sulaa Health Center, from April - August 2019. The population in this study were all pregnant women registered in the KIA book. The research sample consisted of 60 respondents using inclusion criteria. The data analysis uses univariate analysis. The results showed there were differences in the value of the fetal heart rate measurements for each position. The average value (min-max) of DJJ measurement with the lying position (supine) 128-158 times per-minute, mean value 138.81 times per-minute; sitting position 124-158 times per-minute, mean value 143.41 times per-minute; standing position 126-159 times per-minute, mean value 145.58 times per minute. In a sitting and lying position, the resulting heart rate is in the normal range of 120-140 times per-minute; in a standing position, the heart rate obtained 150-160 times per-minute has the potential for tachycardia. The conclusion of this study is that the position of pregnant women affects the results of fetal heart rate measurement and the good position of the FHR measurement when lying on her back
Downloads
References
World Health Organization. Newborns: Reducing Mortality [Internet]. 2019. Available from: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/newborns-reducing-mortality
Kementerian Kesehatan R.I. Dukung Ibu Bekerja Beri ASI Eksklusif [Internet]. Kementerian Kesehatan R.I. 2015. Available from: https://www.kemkes.go.id/article/view/15091400003/dukung-ibu-bekerja-beri-asi-eksklusif.html
Bobak IM, Wijayarini MA, Anugerah PI, Jensen MD, Lowdermilk DL. Buku Ajar Keperawatan Maternitas. Jakarta: EGC; 2005.
Gondo HK, Ewardewa TGA. Kardiotokografi Mengerti dan Memahami Pemantauan Denyut Jantung Janin [Internet]. Suyono J, editor. Jakarta: EGC; 2010. Available from: https://onesearch.id/Record/IOS13415.INLIS000000000041993
Prawirohardjo S. Ilmu Kebidanan. Jakarta: Yayasan Bina Pustaka Sarwono Prawirohardjo; 2008.
Sinaga AD, Purwarini J, Anggraeni LD. The Experiences of Mothers with Intrauterine Fetal Death/Demise (IUFD) in Indonesia. Nurse Media J Nurs. 2020;10(1):86–95.
Endjun JJ, Santana S, Resistantie N. Standarisasi Pemantauan Kesejahteraan Janin [Internet]. Jakarta; 2015. Available from: https://studylibid.com/doc/528152/standarisasi-pemantauan-kesejahteraan-janin
Manuaba IBG. Ilmu Kebidanan, Penyakit Kandungan, dan Keluarga Berencana. Jakarta: EGC; 2010.
Chabibah N, Laela EN. Perbedaan Frekuensi Denyut Jantung Janin Berdasarkan Paritas dan Usia Kehamilan. Siklus J Res Midwifery Politek Tegal [Internet]. 2017 Feb 2;6(1):195–8. Available from: https://ejournal.poltektegal.ac.id/index.php/siklus/article/view/471
Dinas Kesehatan Propinsi Sulawesi Tenggara. Profil Kesehatan Sulawesi Tenggara Tahun 2012. Kendari: Dinas Kesehatan Propinsi Sulawesi Tenggara; 2013.
Dinas Kesehatan Propinsi Sulawesi Tenggara. Profil Kesehatan Sulawesi Tenggara Tahun 2013. Kendari: Dinas Kesehatan Propinsi Sulawesi Tenggara; 2014.
Dinas Kesehatan Propinsi Sulawesi Tenggara. Profil Kesehatan Sulawesi Tenggara Tahun 2014. Kendari: Dinas Kesehatan Propinsi Sulawesi Tenggara; 2015.
Dinas Kesehatan Propinsi Sulawesi Tenggara. Profil Kesehatan Sulawesi Tenggara Tahun 2015. Kendari: Dinas Kesehatan Propinsi Sulawesi Tenggara; 2016.
Dinas Kesehatan Propinsi Sulawesi Tenggara. Profil Kesehatan Sulawesi Tenggara Tahun 2016. Kendari: Dinas Kesehatan Propinsi Sulawesi Tenggara; 2017.
Wahyuni C. Candra Wahyuni. J Qual Women’s Heal [Internet]. 2018;1(1). Available from: https://jqwh.org/index.php/JQWH/article/view/6
Widmaier E, Raff H, Strang K. Vander’s Human Physiology: The Mechanisms of Body Function. 12th ed. New York: McGraw-Hill Education; 2008.
Manembu M, Rumampuk J, Danes VR. Pengaruh Posisi Duduk Dan Berdiri Terhadap Tekanan Darah Sistolik Dan Diastolik Pada Pegawai Negeri Sipil Kabupaten Minahasa. J e-Biomedik [Internet]. 2015 Sep 11;3(3). Available from: https://ejournal.unsrat.ac.id/index.php/ebiomedik/article/view/10150
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
Copyright (c) 2020 Authors

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 4.0 International License.
Authors who publish with Jurnal Bidan Cerdas agree to the following terms:
- Authors retain copyright and grant the journal right of first publication with the work simultaneously licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY-SA 4.0) that allows others to share the work with an acknowledgment of the work's authorship and initial publication in this journal.
- Authors are able to enter into separate, additional contractual arrangements for the non-exclusive distribution of the journal's published version of the work (e.g., post it to an institutional repository or publish it in a book), with an acknowledgment of its initial publication in this journal.
- Authors are permitted and encouraged to post their work online (e.g., in institutional repositories or on their website) prior to and during the submission process, as it can lead to productive exchanges, as well as earlier and greater citation of published work.

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-Share Alike 4.0 International License
You are free to:
- Share, copy and redistribute the material in any medium or format
- Adapt, remix, transform, and build upon the material for any purpose, even commercially.
- The licensor cannot revoke these freedoms as long as you follow the license terms.




